Tips for parallelization in GRASS GIS
in the context of land change modeling

Anna Petrasova, Vaclav Petras
NCSU GeoForAll Lab
at the
Center for Geospatial Analytics
NC State University
Anna Petrasova
- Geospatial Research Software Engineer at the Center for Geospatial Analytics, NC State University
- GRASS GIS Development Team Member
- GRASS GIS Project Steering Committee Member
- Open Source Geospatial Foundation Charter Member
GRASS GIS
- Open-source GIS and geoprocessing engine
- Processing tools: 400+ in core, 400+ addons
- Interfaces: graphical, command line, Python, C
- 3rd party interfaces: actinia (REST API), R, QGIS, OGC WPS
Intro to GRASS parallelization
Tool-level parallelization
r.neighbors input=elevation output=elevation_smoothed size=15 nprocs=4
Workflow-level parallelization
r.grow.distance input=roads distance=dist_to_roads &
r.grow.distance input=water distance=dist_to_water &
r.grow.distance input=forest distance=dist_to_forest &

Multi-threading with OpenMP
- parallelization of geospatial algorithms in C
- relatively easy integration into existing source code
- single code base for all platforms
#pragma omp parallel if(threaded) private(row, col, i)
{
int t_id = 0;
#if defined(_OPENMP)
t_id = omp_get_thread_num();
#endif
struct input *in = inputs[t_id];
DCELL *val = values[t_id];
...
OpenMP-enabled tools (GRASS GIS 8.2)
 r.slope.aspect
r.slope.aspect
 r.neighbors
r.neighbors
 r.mfilter
r.mfilter
 r.series
r.series
 r.patch
r.patch
 r.sun
r.sun
 v.surf.rst
v.surf.rst
 r.sim.water
r.sim.water
 r.sim.sediment
r.sim.sediment
Even more OpenMP-enabled tools
More tools coming in GRASS GIS 8.3:
 r.resamp.interp
r.resamp.interp
 r.resamp.filter
r.resamp.filter
 r.univar
r.univar
Authors of OpenMP code:
Hofierka et al. 2017 and
Aaron Saw Min Sern (GSoC 2021)
Multi-processing with Python
- multiprocessing package and others
- separate OS processes
from multiprocessing import Pool
def compute(value):
# do something with the value
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
pool.map_async(compute, range(0, 10))
r.sun.daily, r.in.usgs, t.rast.what, r.viewshed.exposure, ...
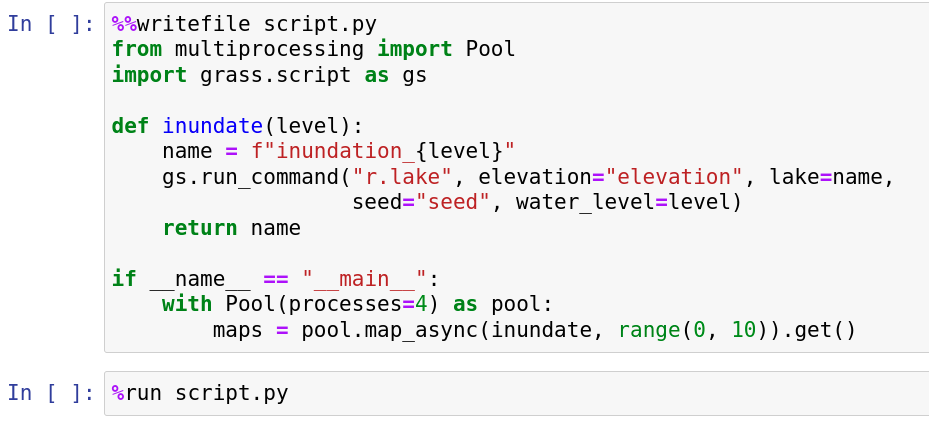
Multiple independent tasks: Python
from multiprocessing import Pool
import grass.script as gs
def inundate(level):
name = f"inundation_{level}"
gs.run_command("r.lake", elevation="elevation", lake=name,
seed="seed", water_level=level)
return name
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
maps = pool.map_async(inundate, range(0, 10)).get()
Multiple independent tasks: Bash
Run tasks in the background:
r.grow.distance input=roads distance=dist_to_roads &
r.grow.distance input=water distance=dist_to_water &
r.grow.distance input=forest distance=dist_to_forest &
Run tasks with GNU Parallel (or alternatives)
echo r.grow.distance input=roads distance=dist_to_roads > jobs.txt
echo r.grow.distance input=water distance=dist_to_water >> jobs.txt
echo r.grow.distance input=forest distance=dist_to_forest >> jobs.txt
parallel --jobs 3 < jobs.txt
Run "hybrid" tasks:
r.neighbors input=forest output=forest_percentage size=37 nprocs=4 &
r.neighbors input=wetland output=wetland_percentage size=37 nprocs=4 &
Tiling approach
from grass.pygrass.modules.grid import GridModule
grd = GridModule("v.to.rast", input="roads", output="roads",
use="val", processes=4)
grd.run()
r.mapcalc.tiled "log_dist = if (dist == 0, 0, log(dist))" nprocs=4
Tips & Tricks & Benchmarks
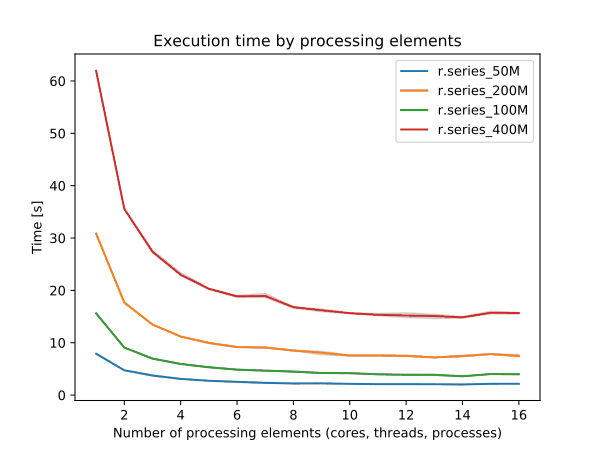
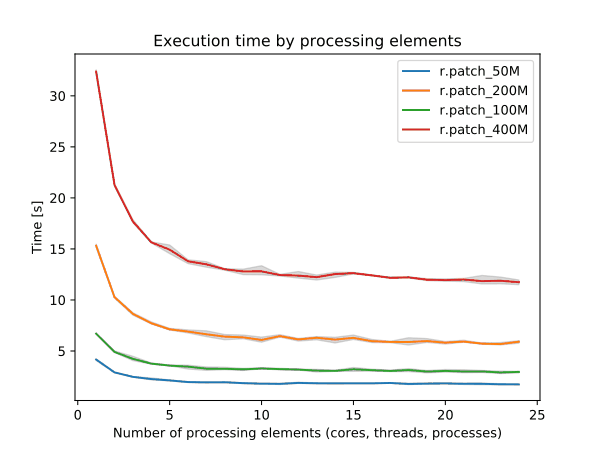
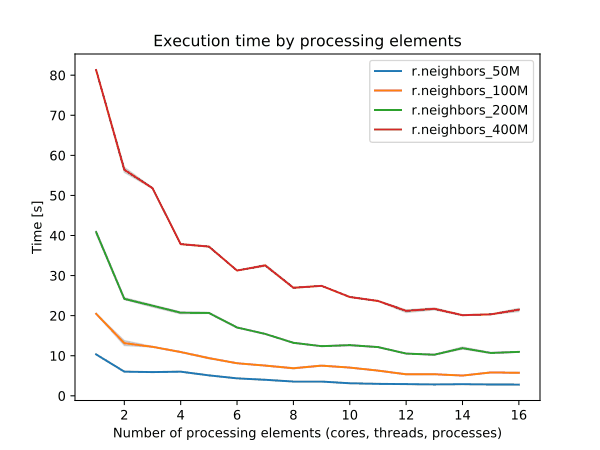
r.neighbors benchmark 400 million cells
\[\mbox{parallel efficiency} = \frac{\mbox{serial processing time}}{N \times \mbox{parallel processing time with N cores}} \]
➨ Use more cores for r.neighbors and r.mfilter with large window sizes.
Even more benchmarks in manual pages
(derived with GRASS Benchmarking library)
➨ Use 4 cores to get most speed improvements with high parallel efficiency.
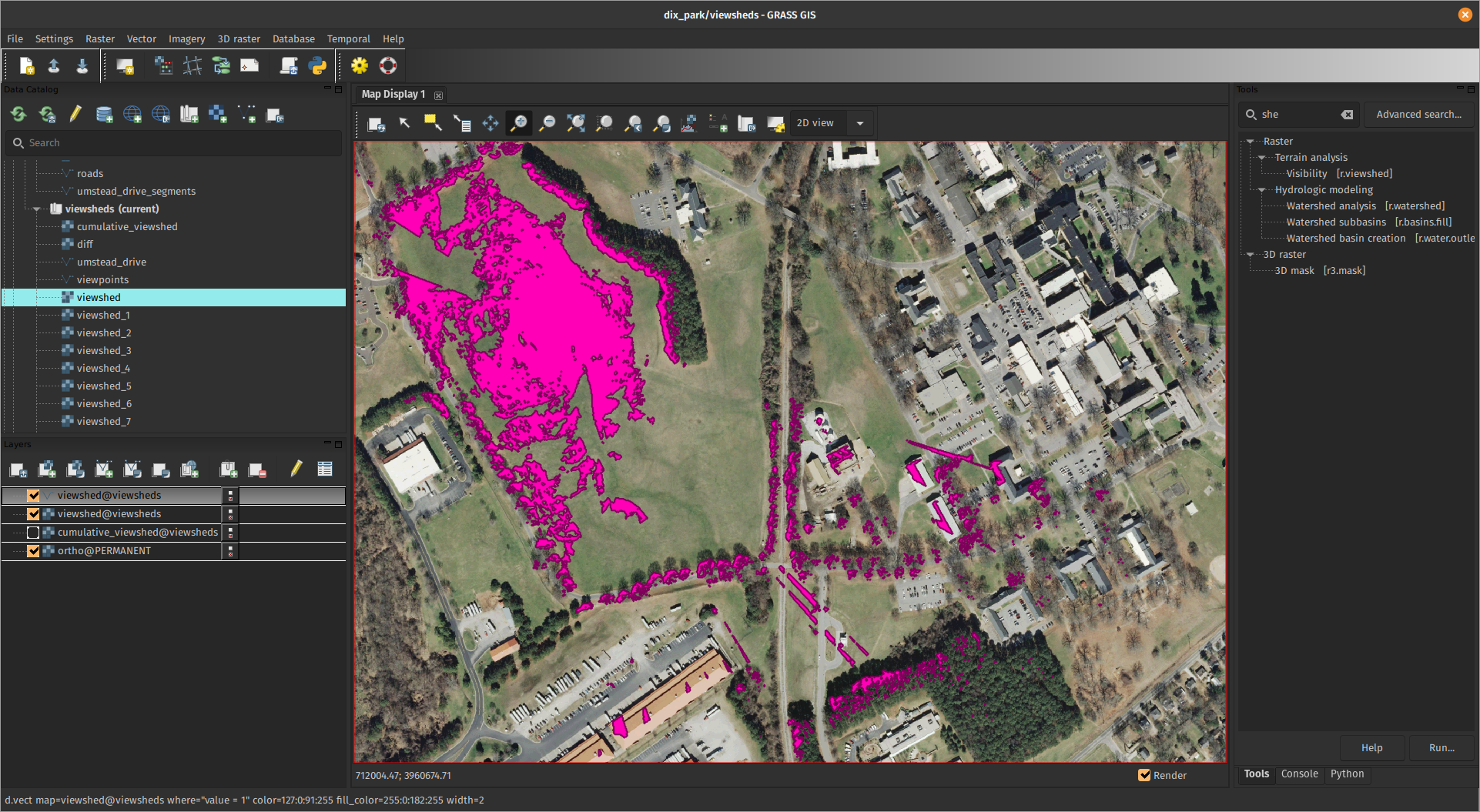
Multiple tasks with different region
import os
from multiprocessing import Pool
import grass.script as gs
def viewshed(point):
x, y, cat = point
name = f"viewshed_{cat}"
os.environ["GRASS_REGION"] = gs.region_env(e=x + 300, w=x - 300,
n=y + 300, s=y - 300,
align="elevation")
gs.run_command("r.viewshed", input="elevation", output=name,
coordinates=(x, y), max_distance=300)
return name
# viewpoints = [(x1, y1, category1), (x2, y2, category2), ...]
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
maps = pool.map_async(viewshed, viewpoints).get()
Multiple tasks with different region
import os
from multiprocessing import Pool
import grass.script as gs
def viewshed(point):
x, y, cat = point
name = f"viewshed_{cat}"
os.environ["GRASS_REGION"] = gs.region_env(e=x + 300, w=x - 300,
n=y + 300, s=y - 300,
align="elevation")
gs.run_command("r.viewshed", input="elevation", output=name,
coordinates=(x, y), max_distance=300)
return name
# viewpoints = [(x1, y1, category1), (x2, y2, category2), ...]
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
maps = pool.map_async(viewshed, viewpoints).get()
Multiple tasks with different region
import os
from multiprocessing import Pool
import grass.script as gs
def viewshed(point):
x, y, cat = point
name = f"viewshed_{cat}"
env = os.environ.copy()
env["GRASS_REGION"] = gs.region_env(e=x + 300, w=x - 300,
n=y + 300, s=y - 300,
align="elevation")
gs.run_command("r.viewshed", input="elevation", output=name,
coordinates=(x, y), max_distance=300, env=env)
return name
# viewpoints = [(x1, y1, category1), (x2, y2, category2), ...]
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
maps = pool.map_async(viewshed, viewpoints).get()
Tiling approach: large overhead
Overhead from merging data and I/O:
| process (12 cores, 2 billion cells) | run time (MM:SS) | speedup | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| rasterization with GridModule | 00:35 | 1.9 | 16 % |
| r.mapcalc.tiled (simple expression) | 00:39 | 1.8 | 15 % |
➨Use for large data
➨Long running in-memory computations
➨ Use r.mapcalc.tiled for complex raster algebra expressions
Tiling approach: tiling scheme

➨Slice data horizontally
Running GRASS in non-interactive session
Run module in existing mapset:
grass ~/grassdata/US_albers/visibility --exec r.viewshed input=elevation ...
Run module in a newly created mapset:
grass -c ~/grassdata/US_albers/visibility --exec input=elevation ...
Run Python script in existing mapset:
grass ~/grassdata/US_albers/visibility --exec python viewshed_script.py
Run Python script in a temporary mapset:
grass --tmp-mapset ~/grassdata/US_albers/ --exec python viewshed_script.py
Running GRASS commands in parallel
Generate commands:
jobs.sh
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis1 --exec python myscript.py 1
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis2 --exec python myscript.py 2
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis3 --exec python myscript.py 3
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis4 --exec python myscript.py 4
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis5 --exec python myscript.py 5
grass ~/grassdata/nc_spm_08_grass7/analysis6 --exec python myscript.py 6
...
Run in parallel:
parallel --jobs 8 < jobs.sh
Caveats: r.mask
➨ Do not use mask in parallel within the same mapset:
from multiprocessing import Pool
import grass.script as gs
def process(category):
gs.run_command("r.mask", raster=f"mask_{category}")
# do some other stuff
with Pool(processes=4) as pool:
maps = pool.map_async(process, range(0, 10)).get()
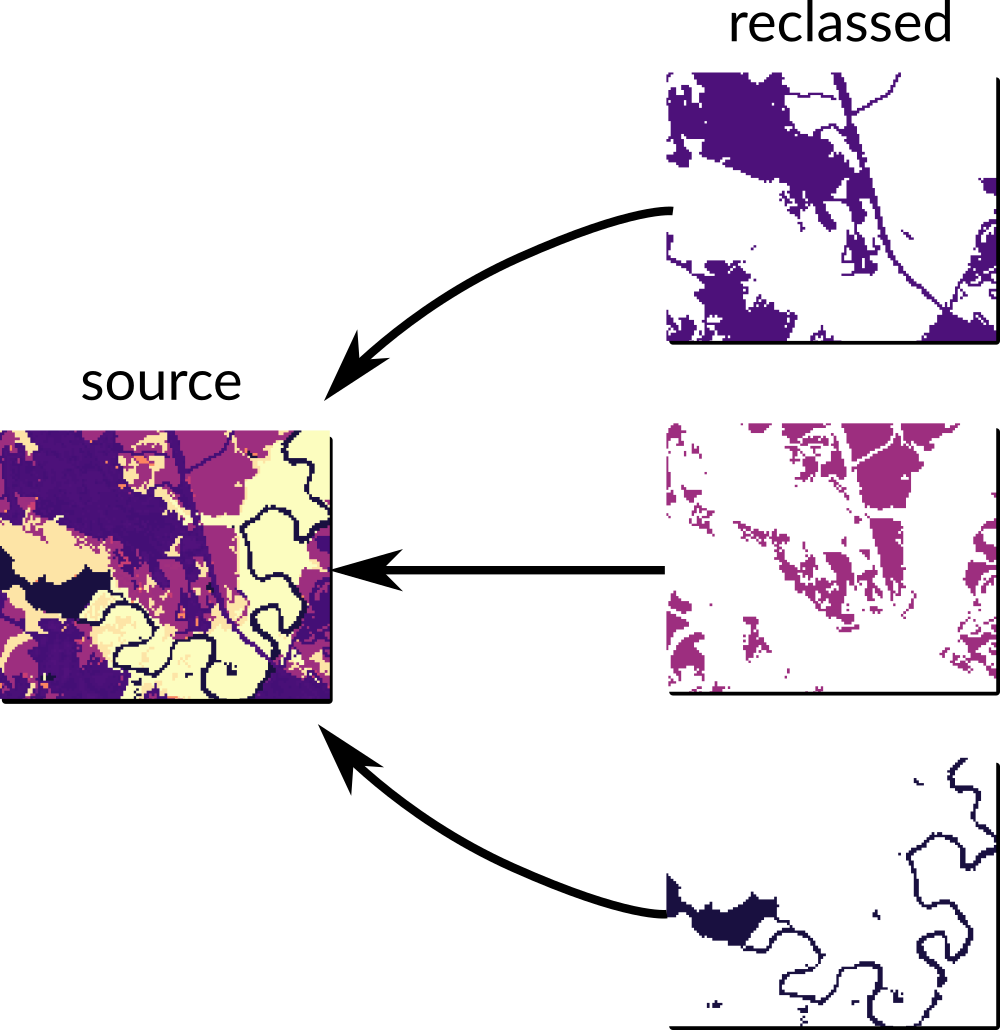
Caveats: r.reclass
➨ Do not reclassify from the same raster in parallel with r.reclass (creates virtual raster)
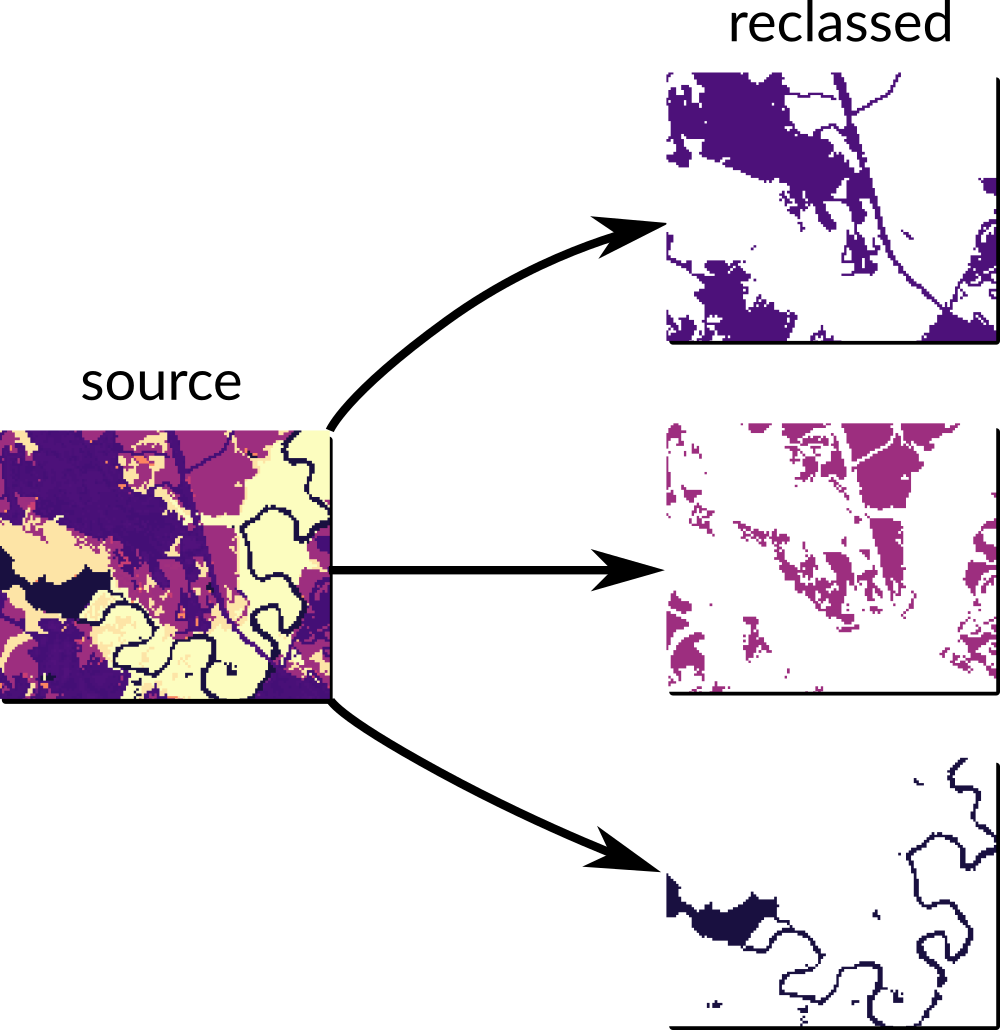

Caveats: r.reclass
➨
r.reclass creates backlinks by editing the raster file.
Instead, use e.g., r.recode to create a copy.

Multiprocessing in Jupyter Notebooks
This may not work from Jupyter Notebook:
Multiprocessing in Jupyter Notebooks
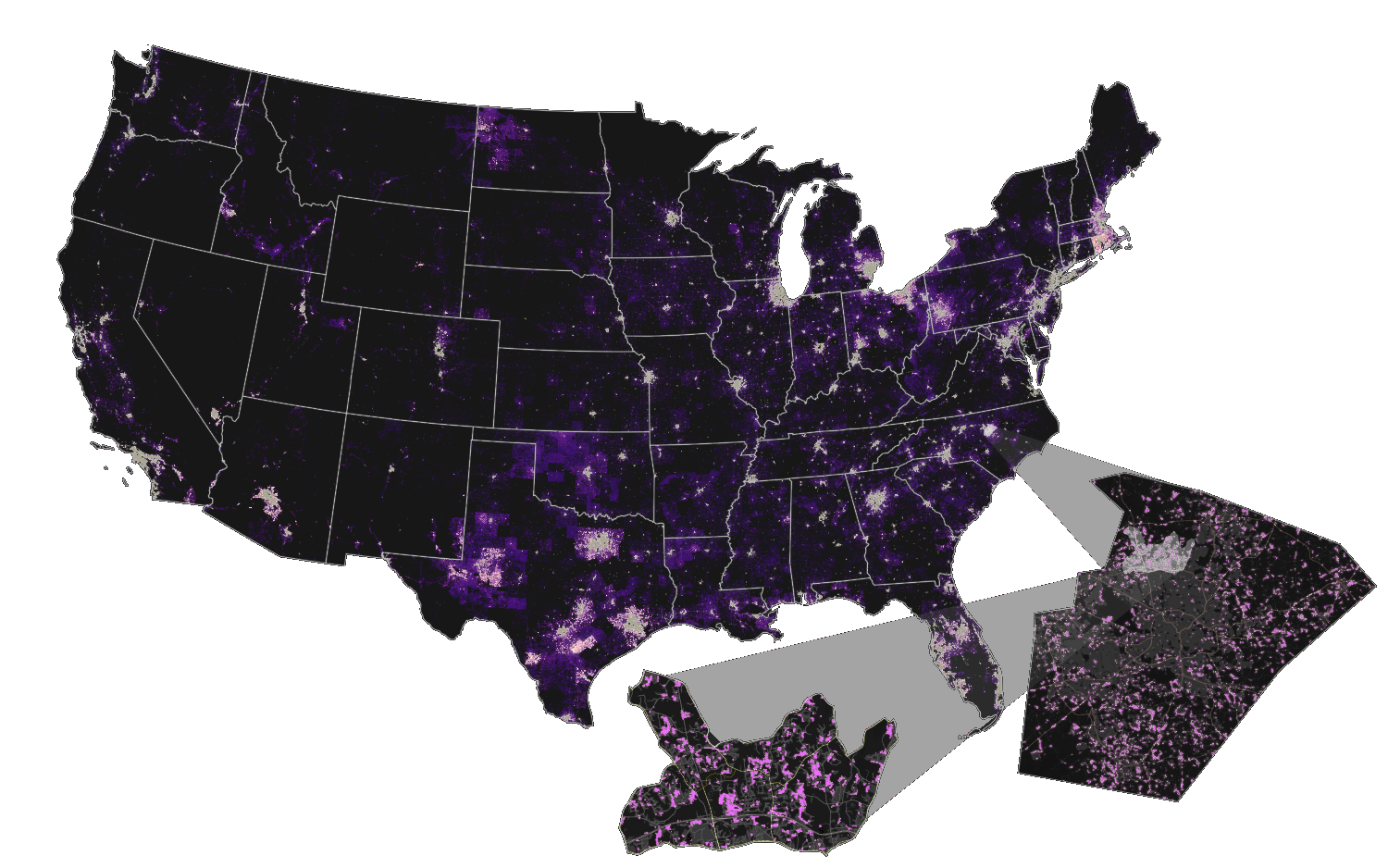
Scaling urban growth model
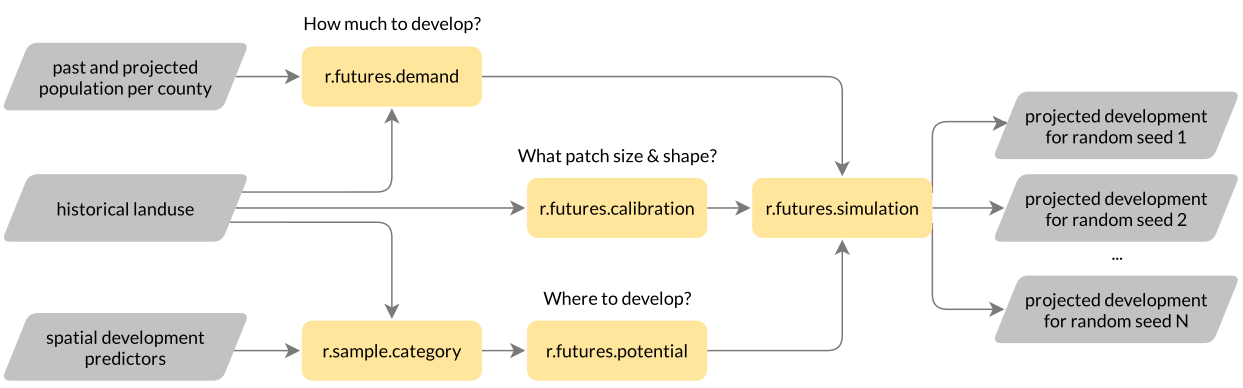
FUTURES
- FUTure Urban-Regional Environment Simulation
- explicitly captures the spatial structure of development
- stochastic, flexible (in terms of predictors, scenarios)
- implemented as r.futures tool set in GRASS Addons
FUTURES case studies
Parallelized workflow for Southeast US at 30 m (2 billion cells)
➨ github.com/petrasovaa/parallel-GRASS-FUTURES-notebook
Scaled up to Contiguous US (16 billion cells) on institutional HPC
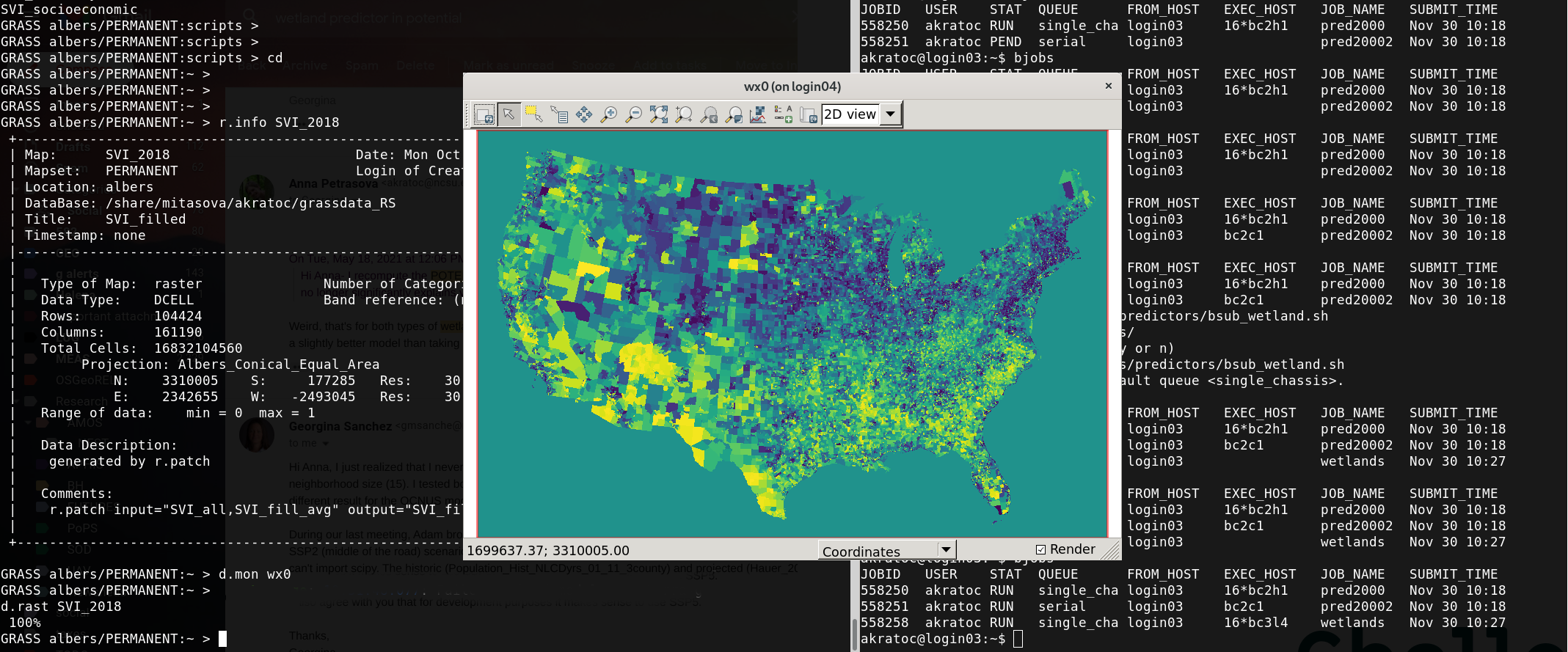
When parallelization matters
r.futures.devpressure (internally uses r.mfilter)
| window size | cores | run time (HH:MM) | serial time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 61 x 61 | 32 | 4:20 | 4.9 days |
When parallelization is less important
| tool | cores | run time (MM:SS) | serial time (MM:SS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| r.slope.aspect | 12 | 11:54 | 36:50 |
| r.mapcalc.tiled | 12 | 09:44 | 20:33 |
Parallelization by US states
- simulation doesn't fit into memory
- simulation itself is not parallelized
- we need a lot of stochastic runs
50 states x 50 stochastic runs => 2500 cores
Parallelization by US states
Distribute tasks across nodes using MPI (Message Passing Interface):
jobs.txt
grass ~/grassdata/albers/state_1 --exec r.futures.simulation subregions=state_1 ...
grass ~/grassdata/albers/state_2 --exec r.futures.simulation subregions=state_2 ...
grass ~/grassdata/albers/state_3 --exec r.futures.simulation subregions=state_3 ...
submit.sh
mpiexec python -m mpi4py -m pynodelauncher jobs.txt
github.com/ncsu-landscape-dynamics/pynodelauncher
Parallelization by US states
Gets tricky if some processes take much longer than others (looking at you, Texas)
texasproud.com/how-big-is-texas-its-huge
Parallelization by US states
Gets tricky if some processes take much longer than others (looking at you, Texas)
texasproud.com/how-big-is-texas-its-huge
Results
Atlanta
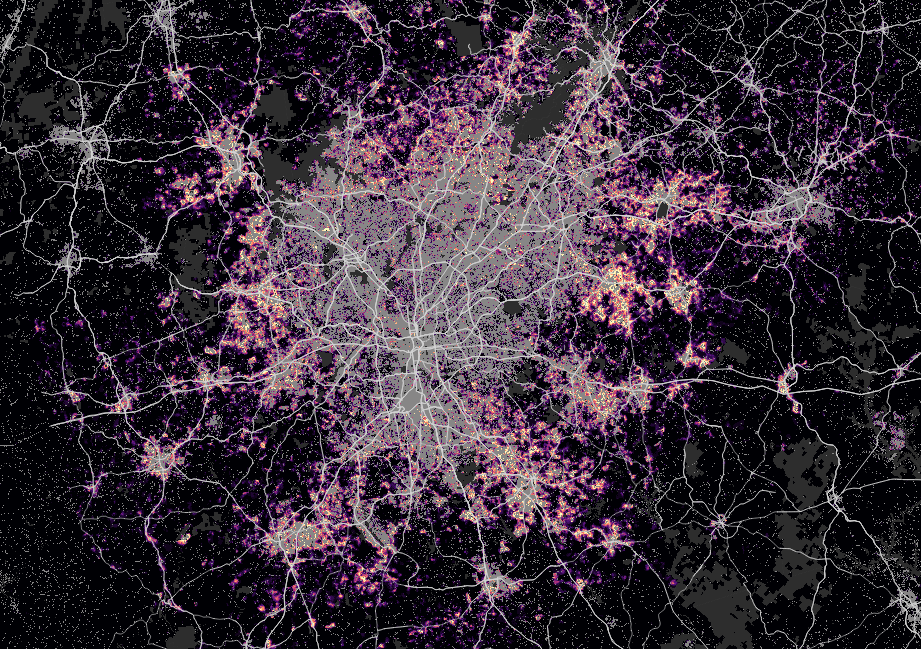
New York
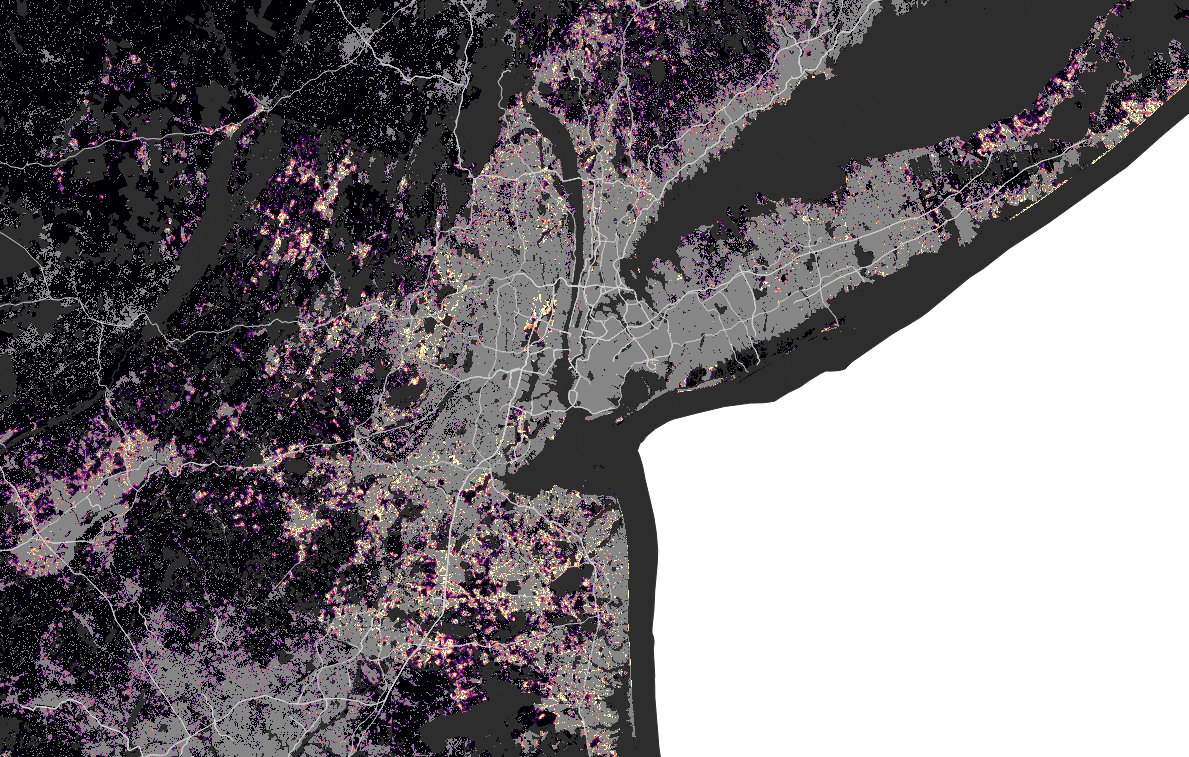
San Francisco
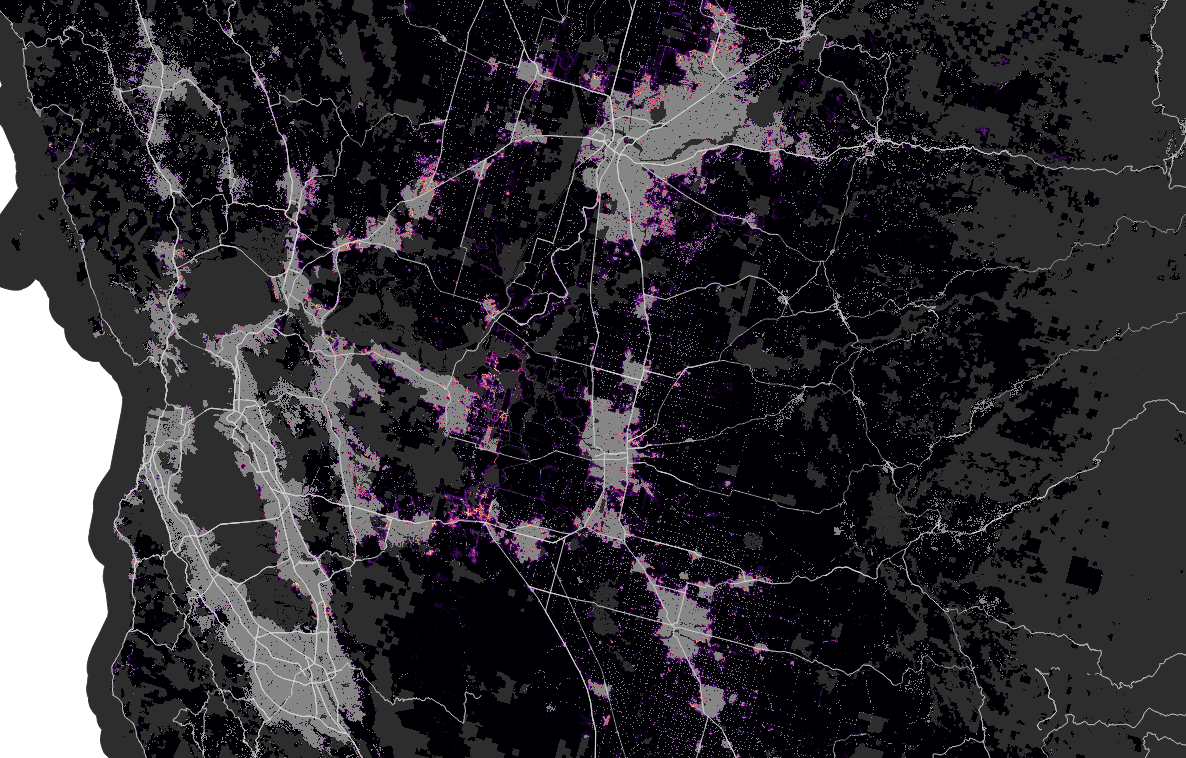
Phoenix
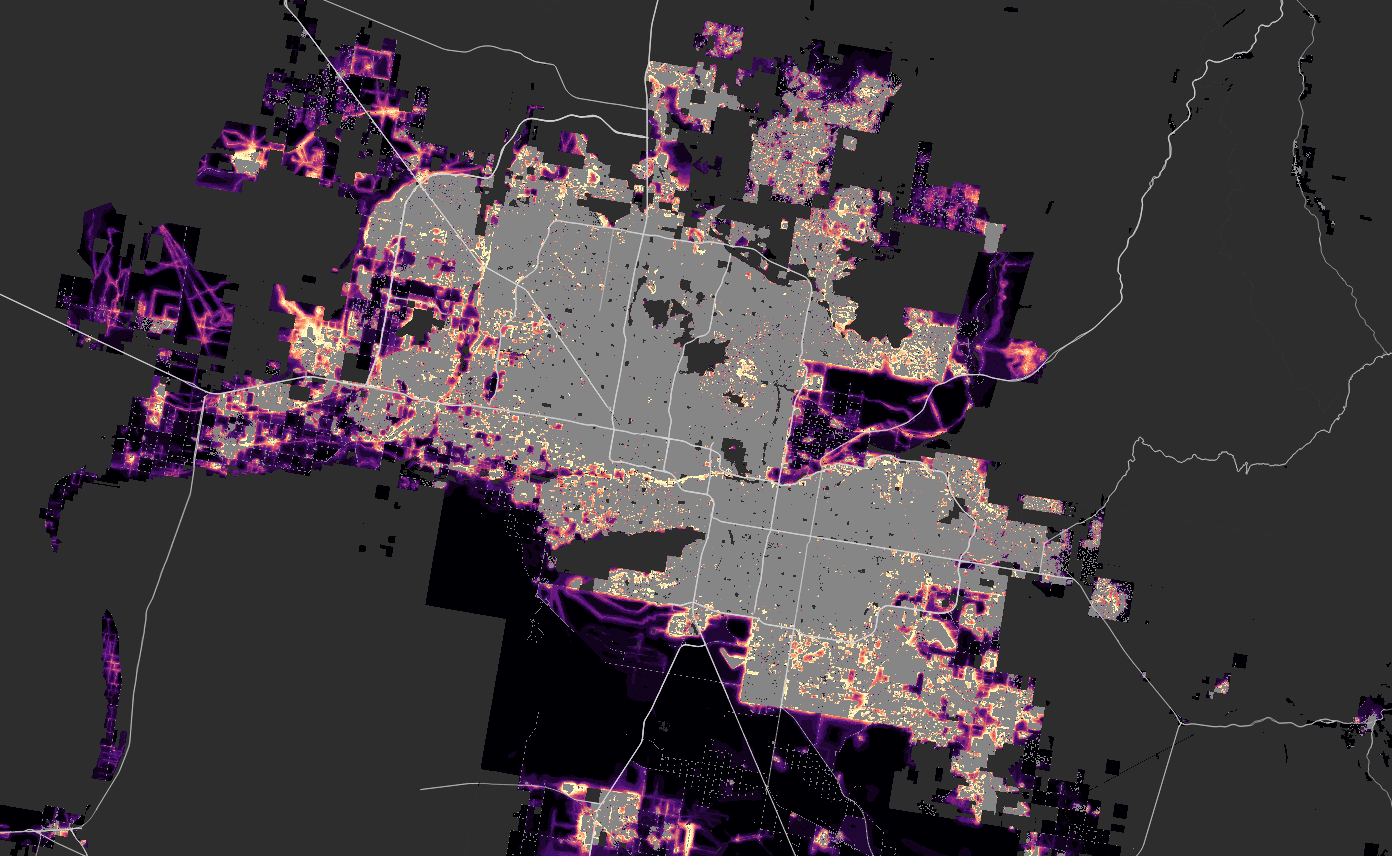
Houston
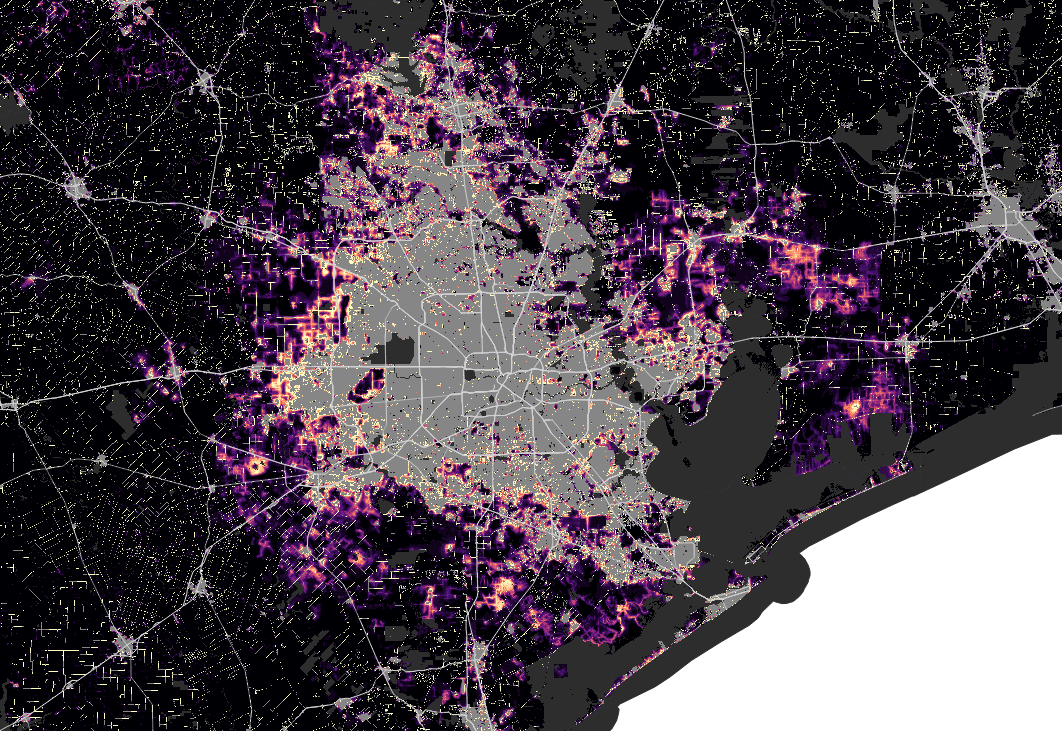
Resources
More benchmarks
12 cores, 2 billion cells Southeast US at 30 m resolution, System76 Thelio with Ubuntu 20.04
| tool | window size | run time (MM:SS) | speedup | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r.slope.aspect | 3 x 3 | 00:32 | 2.7 | 22.6 % |
| r.neighbors | 37 x 37 | 09:16 | 10.1 | 83.8 % |
| r.mfilter | 61 x 61 | 48:33 | 11.2 | 93.4 % |